|
W E A T H E R
Weather and climate changes
Influence of pressure units on the climate changes: The European climate is affected mainly by the circulatory pressure units - the Iceland’s cyclone and the Azorean anticyclone. A small atmospheric pressure difference is reflected by a cold winter, a large atmospheric pressure difference is reflected by a temperate winter.
Influence of the variability of the global atmosphere circulation on the climate changes: The variations of the ocean currents circulation and the pressure units also from the Pacific region and Australia are reflected also in changes of the European climate through strong air flows in the higher layers of the atmosphere.
Influence of human activities on the climate changes: The greenhouse effect is amplified due to the increase of the contents of the so called greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, mainly of the carbon dioxide and methane. Their concentration in the atmosphere has increased compared to the year 1750 by 33% and 152%, respectively. The greenhouse gases absorb heat and return it back to the Earth similarly to a greenhouse and due to this they contribute to warming.
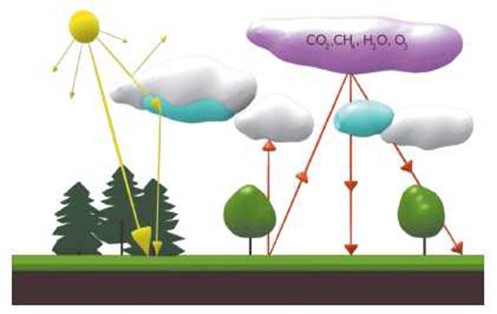
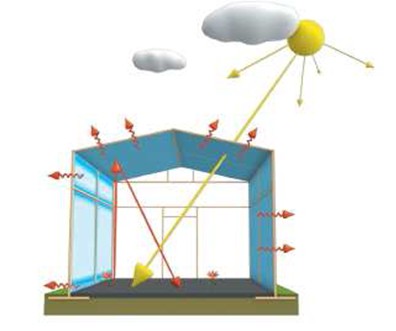
Negative effects of the human activities upon climate: The climate changes except by the greenhouse gases are affected in a negative way by transportation, industrial production, air pollution, fertilizers, agricultural production, burning down of savannas, old-growth forests, plastic and pesticide manufacturing, etc. The negative effects of these activities show themselves by acid precipitation,thinning away of the ozonosphere (blue and purple colour), i.e. of the atmospheric layer that protects us from the harmful ultraviolet solar radiation.
Impacts of the climate changes: Global warming during the time period from 4 to 1 thousand years BC: deciduous forests in Scandinavia, in the 13th century BC the large streams Rhine, Danube, Pad, Euphrates, Don, Ganges dried up, the cold harsh climate in the middle of the 1st millennium – considerable temperature reduction, the nations living on the Asian steppes come to the European lowlands, the migration period (barbarian invasions), coming of the Slavs to central and southern Europe.
11th to 13th century – extremely warm climate, sufficiently humid, onset of prosperity, the green land – Gronland – is populated.
Negative effects of the climate changes: Since 1306 a sequence of harsh winters, cold summers – bad crops, plague, wars – the European population decreased by one half. Warming follows as late as 1470, exact evidence about the backdown of glaciers, devastating fluds on the Danube in 1501, 1530 – Netherlands – the population decreased by 400 000, 1590-1850 – little ice age – from time to time even the Adriatic freezes over, since that time the trend has been towards warming.
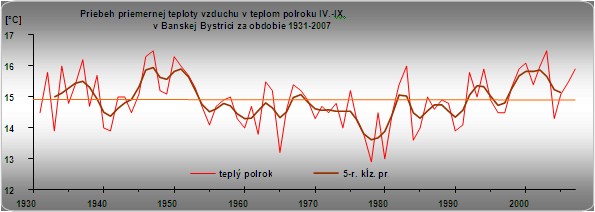
The climate changes are evident. They are caused by mutual complex bonds between the natural and human factors and at the present time they manifest themselves through regional differences.
Climate is naturally changeable. Changes alternate in cycles in the intervals 2-3, 7-11, 20-30, 90, 180-200, 400, 1000, 2 500, 23 000, 41 000, 100 000 years.
Human activities bring certain amount of instability in the natural climate change cycles.
It is possible to make the negative effects of the climate changes less severe by reducing the human activities which in the long term contaminate, expose to stress, damage the health of and weaken the nature (less coal, oil, energy, products, consumer goods, transportation, etc.).
Workshop Material
Lecturer
- RNDr. Štefan Soták (Slovenský hydrometeorologický ústav, Banská Bystrica)
Return to the project introduction page.
|







